Ground Electrical and Electromagnetic Studies in Koyna-Warna Region, India
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0780-yAbstract
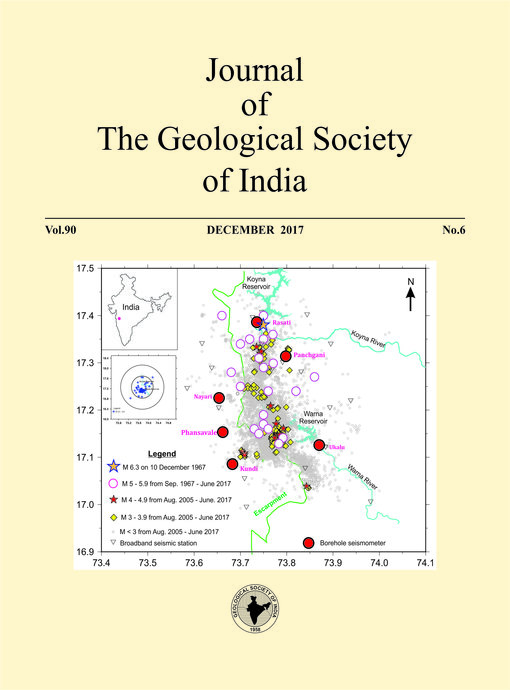
In this paper, we present results of the Ground Electrical and Electromagnetic (GEE) studies (MT, CSAMT, DRS) carried out in the Koyna-Warna zone since 1976 and discuss their relevance in understanding the seismicity of the Koyna-Warna seismic zone. Though there were not many GEE studies carried out in this region, the existing ones provided a vital information, in particular, on the subsurface crustal structure, the Deccan Trap thickness and its variation and also the nature of the basement in this region. The GEE studies rule out the presence of any subtrappean sediments in this region. An interesting feature that has been identified from MT studies is the presence of a well-defined crustal block structure, characterized by high resistive blocks interspersed with moderately conductive features. All these structural features clearly point out to the intensity of tectonic disturbance that the region was subjected to in the geological past. The conductive features are correlatable with some of the known seismogenic structural features, for e.g., the Konya Fault Zone, the west coast fault, the Donachiwada fault. The moderately resistive zone sitting over the high resistive blocks as seen both in MT& DRS models is inferred to be related to the generally fractured nature of the shallow crustal column. The conductive linear features bordering the resistive blocks represent fluid filled fracture/fault zones. It is inferred that because of the NE to NS oriented compressive stress regime in the Indian shield, due to the Himalayan collision tectonics, some of these structural features may become the locales of stress accumulation which may get released due to fluid filling of these zones under the influence of nearby reservoirs, resulting in triggering of seismicity.
Results from different GEE studies conducted in the study area are found to be highly consistent with each other as well as with the Rasati bore hole data, thus bringing significant validity to the subsurface model derived. Further, the 3D modelling of the MT data acquired in the Koyna-Warna region together with airborne gravity gradient and magnetic studies carried out under the Deep drilling program would open up new gate ways to accomplish multi-parametric three dimensional modeling, that will provide still more detailed and relevant subsurface image of this important RTS zone.
Downloads
Metrics
Issue
Section
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
References
Athavale, R.N. and Mohan, I. (1976) A Technical Report on Integrated Geophysical Studies in the Koyna Hydroelectric Project Area of Maharashtra State. NGRI, India and CEG, Hyderabad.
Borah, U.K., Patro, P.K. and Suresh, V. (2015) Processing of noisy magnetotelluric time series from Koyna-Warna seismic region, India: a systematic approach. Annals of Geophysics, 58, 2, G0222; doi:10.4401/ ag-6690.
Deshpande, B.G. and Jagtap, P.N. (1971) Interpretation of aerial photographs of Koyna Region. In Symposium on Koyna Earthquake. Indian Jour. Power and River Valley Development, pp.25–26.
Duncan, R.A. and Pyle, D.G. (1988) Rapid eruption of Deccan flood basalts at the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary. Nature, v.333, pp.841–843.
Durá-Gómez, I. and Talwani, P. (2010) Reservoir-induced seismicity associated with the Itoiz Reservoir, Spain: a case study. Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.181, pp.343–356. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04462.x.
Dziewonski, A.M., Ekstrom, G., Franzen, J.E. and Woodhouse, J.H. (1988) Global seismicity of 1980 Centroid moment tensor solutions for 515 earthquakes. Physics Earth Planet. Inter., v.50, pp.127–154.
Geological Survey of India (1968) A Geological Report on the Koyna Earthquake of 11th December 1967, Satara District, Maharashtra State. Unpublished Report, 242p.
Gowd, T.N., Rao, S.V.S., and Gaur, V.K. (1992) Tectonic stress field in the Indian subcontinent. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.97(B8), pp.11879–11888, doi:10.1029/91JB03177.
Gupta, H.K., Narain, H., Rastogi, B.K. and Mohan, I. (1969) A study of the Koyna earthquake of December 10, 1967. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.59, pp.1149–1162.
Gupta, H.K., Rastogi, B.K. and Narain, H. (1972) Common features of the reservoir associated seismic activities. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.62, pp.481–492.
Gupta, H.K. and Rastogi, B.K. (1974) Will another damaging earthquake occur in Koyna? Nature, v.248, pp.215–216.
Gupta, H.K., Rao, R.U.M., Srinivisan, R., Rao, G.V., Reddy, G.K., Dwivedy, K.K., Banerjee, D.C., Mohanty, R. and Satyasaradhi, Y.R., (1999) Anatomy of surface rupture zones of two stable continental region earthquakes, 1967 Koyna and 1993 Latur, India. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.26(13), pp.1985–1988.
Gupta, H.K. (2002) A review of recent studies of triggered earthquakes by artificial water reservoirs with special emphasis on earthquakes in Koyna, India. Earth Sci. Rev., v.58, pp.279–310
Gupta, H.K., Mandal, P. and Rastogi, B.K. (2002) How long will triggered earthquakes at Koyna, India continue? Curr. Sci., v.82(2), pp.202–210.
Gupta, H.K., Nayak S. and the Koyna Workshop Committee, (2011) Deep scientific drilling to study reservoir-triggered Earthquakes in Koyna, Western India. Scientific Drilling, doi:10.2204/iodp.sd.12.07.2011
Gupta, H., Nayak, S., Ellsworth, W., Rao, Y.J.B., Rajan, S., Bansal, B.K., Purnachandra Rao, N., Roy, S., Arora, K., Mohan, R., Tiwari, V.M., Satyanarayana, H.V.S., Patro, P.K., Shashidhar, D. and Mallika, K. (2014) Probing reservoir-triggered earthquakes in Koyna, India, through scientific deep drilling, Scientific Drilling, v.18, pp.5-9, doi:10.5194/sd-18-52014.
Gupta, H., Rao N.P., Roy S., Arora K., Tiwari V.M., Patro P.K., Satyanarayana H.V.S., Shashidhar D., Mallika K., Akkiraju V.V., Goswami D., Vyas D., Ravi G., Srinivas K.N.S.S.S., Srihari M., Dubey C.P., Raju D.C.V., Borah U., Reddy K.C., Babu N., Rohilla S., Dhar U., Sen M., Rao Y.J.B., Bansal B.K. and Nayak S. (2015) Investigations related to scientific deep drilling to study reservoir-triggered earthquakes at Koyna, India. Internat. Jour Earth Sci., v.104(6), pp.1511-1522, DOI 10.1007/s00531-014-1128-0.
Gupta, H., Arora, K., Rao, N.P., Roy, S., Tiwari, V., Patro, P.K., Satyanarayana, H.V.S., Shashidhar, D., Mahato, C., Srinivas, K.N.S.S.S., Srihari, M., Satyavani, N., Srinu, Y., Gopinadh, D., Raza, H., Monikuntala, J., Akkiraju, V., Goswami, D., Digant, V., Dube, C. P., Raju, D., Bora, U., Kashi, R., Reddy, K.C., Babu, N., Bansal, B.K. and Nayak, S. (2016) Investigations of Continued Reservoir Triggered Seismicity at Koyna, India, Tectonics of the Deccan Large Igneous Province. Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ., no.445, http://doi.org/10.1144/SP445.11
Hansen P.C. (1998) Rank Deficient and Discrete Ill: Posed Problems, Numerical Aspects of Linear Inversion. Soc. for Ind. and Appl. Math., Philadelphia, Penn, 247.
Kaila, K.L., Reddy, P.R., Dixit, M.M. and Lazrenko (1981) Deep crustal structure at Koyna, Maharashtra indicated by deep seismic soundings. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.22, pp.1–16.
Kailasam, L.N., Pant, P.R. and Lahtri, S.M. (1969) Seismic investigations in the earthquake affected areas of Koyna and neighbourhood, Satara District, Maharashtra. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.100, pp.123-126.
Kailasam, L.N. and Murthy, B.G.K., (1971) A short note on gravity and seismic investigations in the Koyna area. In Symposium on Koyna Earthquake. Indian Jour. Power and River Valley Development, pp.27–30.
Kailasam, L.N., Murthy, B.G.K. and Chayanulu, A.Y.S.R. (1972) Regional gravity studies of the Deccan Trap areas of the Peninsular India. Curr. Sci., v.41, pp.403-407
Kailasam L.N., Reddy A.G.B., Rao Joga Sathyamurthy K. and Murthy B.S.R. (1976) Deep electrical resistivity soundings in Deccan trap region. Curr. Sci. v.45, pp.4–16.
Krishna Brahmam, N. and Negi, J.G. (1973) Rift valleys beneath the Deccan trap (India). Geophys. Res. Bull., v.11(3), pp.207–237.
Langston, C.A. (1981) Source Inversion of Seismic Wave Form: The Koyna India Earthquake of 13, September 1967. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer. v.71, pp.1–24.
Langston, C.A. and Franco-Spera, M. (1985) Modeling of Koyna India, aftershock of 12th Dec. 1967. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.75, pp.651–660.
Negi, J.G., Agrawal, P.K. and Rao, K.N.N. (1983) Three-dimensional Model of the Koyna Area of Maharashtra State (India) Based on the Spectral Analysis of Aeromagnetic Data. Geophysics,v. 48, pp.964–974.
Pandey, A.P. and Chadha, R.K. (2003) Surface loading and triggered earthquakes in the Koyna–Warna region, western India. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.139, pp.207–223.
Parker, R.L. and Booker, J.R. (1996) Optimal one-dimensional inversion and bounding of magnetotelluric apparent resistivity and phase measurements. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.98, pp.269–282, doi:10.1016/S00319201(96)03191-3.
Patro, P.K. and Sarma, S.V.S. (2009) Lithospheric electrical imaging of the Deccan trap covered region of western India. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.114, B01102, doi:10.1029/2007JB005572
Rastogi, B.K. and Talwani, P. (1980) Relocation of Koyna earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Amer., v.70, pp.1849-1868.
Rajendran, K. and Harish, C.M. (2000) Mechanism of triggered seismicity at Koyna: An evaluation based on relocated earthquakes. Curr. Sci., v.79(3).
Rao, N.P., Roy, S. and Arora, K. (2013) Deep scientific drilling in Koyna, India – brainstorming workshop on geological investigations 19–20 March 2013. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.81, pp.722–723.
Rao, N.P., et al. (2016) Geophysical and seismological studies in Koyna-Warna region. Technical report No. NGRI-2016-SEISM-907.
Rodi, W. and Mackie, R.L. (2001) Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion, Geophysics, v.66, pp.174–187, doi:10.1190/1.1444893.
Roy, S., Rao, N.P., Akkiraju, V.V., Goswami, D., Sen, M., Gupta, H.K., Bansal, B.K. and Nayak, S. (2013a) Granitic basement below Deccan traps unearthed by drilling in the Koyna Seismic zone, Western India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.81, pp.289–290
Roy, S., Akkiraju, V.V., Goswami, D., Vyas, D., Ravi, G., Purnachandra Rao, N., Sen, M. and Gupta, H. (2013b) First results from borehole investigations at Koyna, India, site of proposed scientific deep drilling to study reservoir triggered seismicity. In: Proceedings of American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, 9–13 December 2013, San Francisco.
Sarma, S.V.S., Patro, B.P.K., Harinarayana, T., Veeraswamy, K., Sastry, R.S. and Sarma, M.V.C. (2004) A magnetotelluric (MT) study across the Koyna seismic zone, western India: evidence for block structure. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.142, pp.23–36.
Shashidhar, D., Satyanarayana, H.V.S., Mahato, C.R., Mallika, K., Rao, N.P. and Gupta, H.K. (2016) Borehole Network at Koyna India. Seismological Research Letters, Advance online publication.
Snow, D.T. (1982) Hydrology of Induced Seismicity and Tectonism: Case Histories of Kariba and Koyna. Geol. Soc. Amer. Special Paper no.189, pp.317–360.
Subba Rao, D.V. (1996). Resolving Bouguer anomalies in continents: a new approach. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.23(24), pp.3543–3546.
Talwani, P. (1997) Seismotectonics of the Koyna–Warna area, India. Pure Appld. Geophys., v.150, pp.511–550.
Yadav, A., Bansal, B.K., Pandey, A.K. (2016) Five decades of triggered earthquakes in Koyna-Warna region, western India – A review. Earth Sci. Rev., v.162, pp.433-450.

 Prasanta K. Patro
Prasanta K. Patro